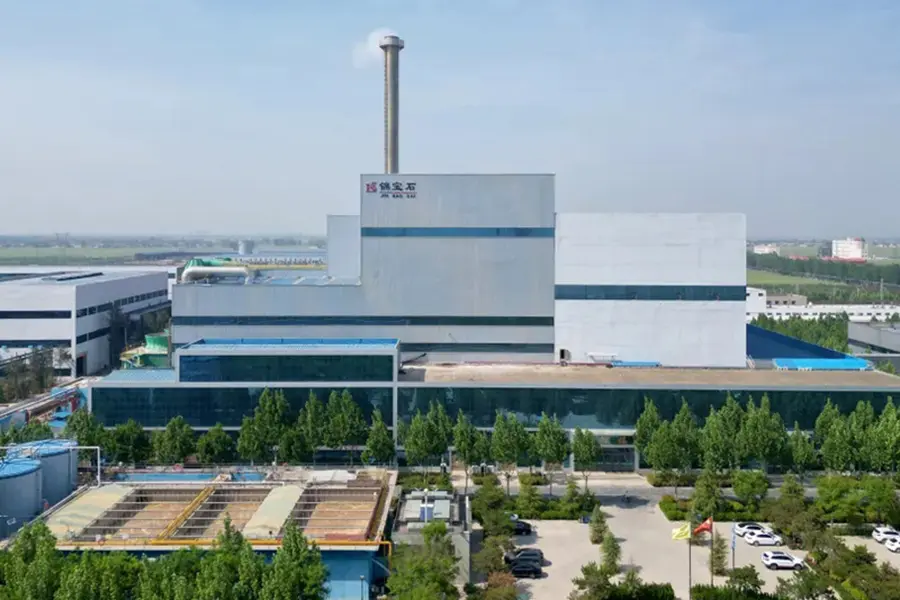
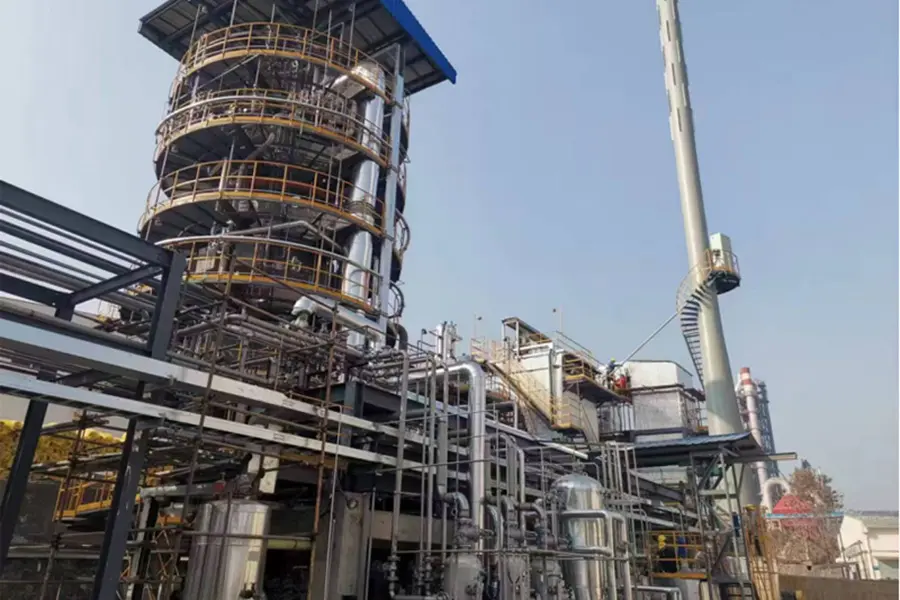
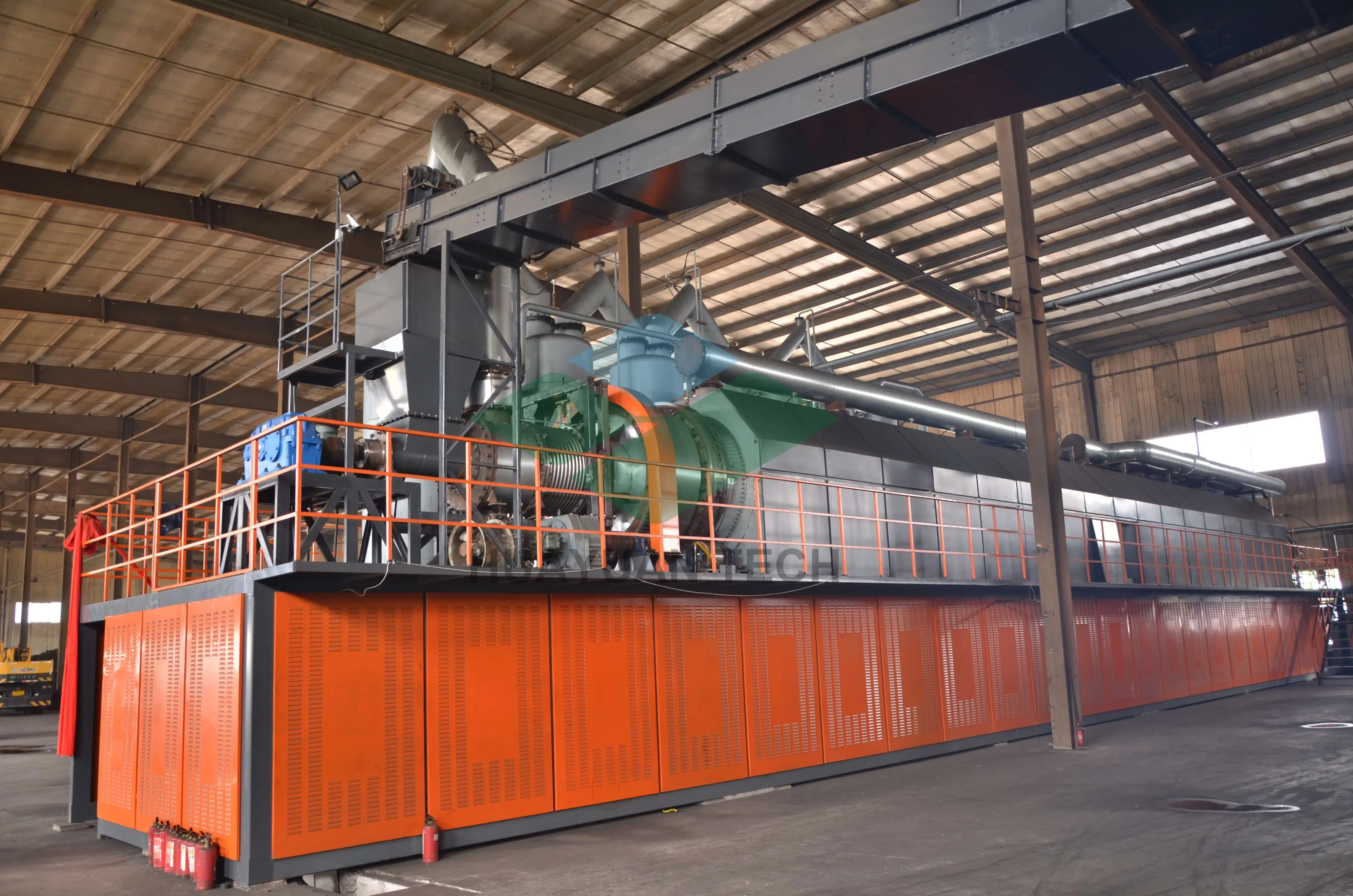
- Continuous Screw Pyrolysis Plant
- Continuous Twin-Screw Pyrolysis Plant
- Continuous Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Plant
- Semi-Continuous Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Plant
- Batch Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Plant
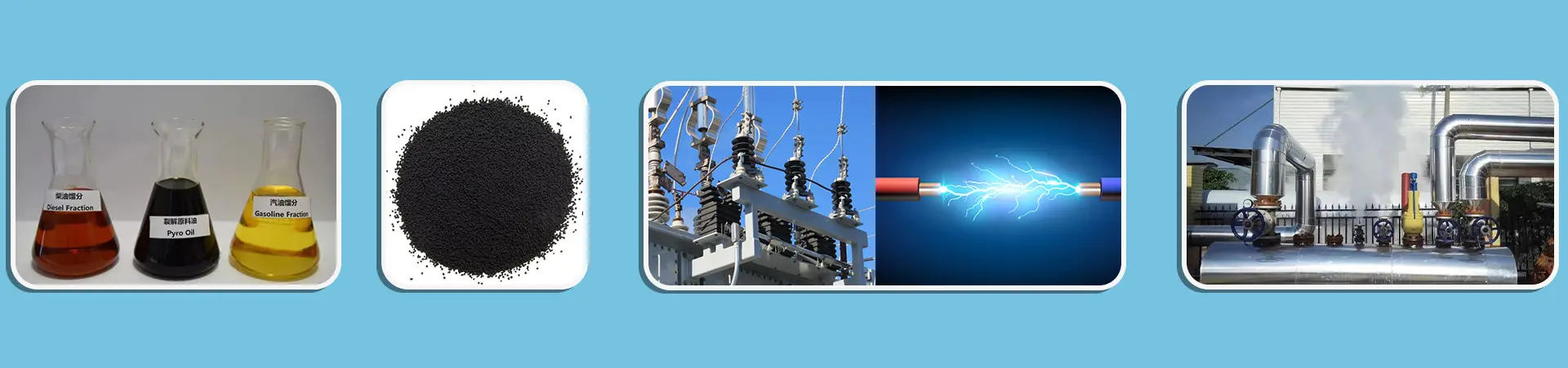
- Recovered Carbon Black Refining Plant
- Pyrolysis Oil Refining Plant
- MSW to Energy Plant
- Industrial Solid Waste to Energy Plant
- Waste Gas to Energy Plant
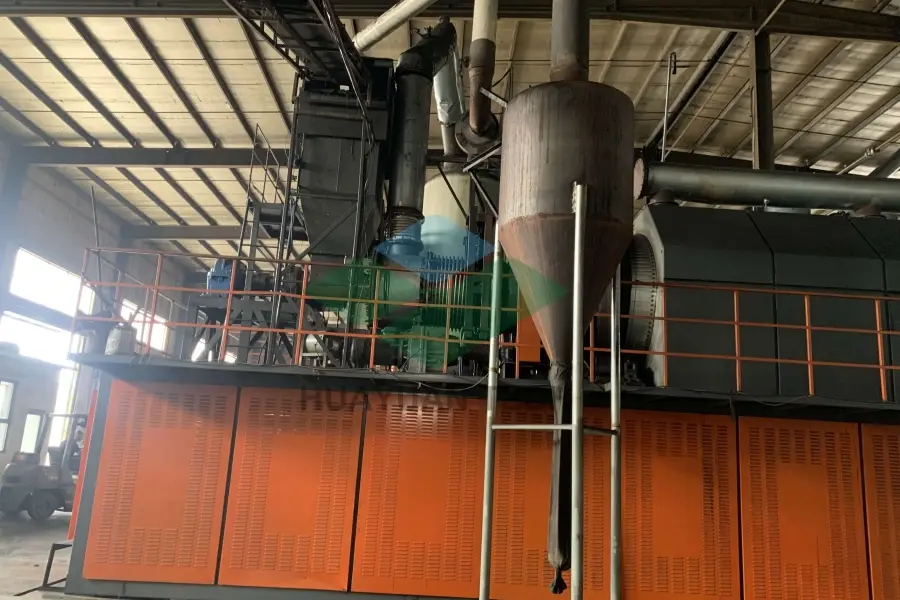
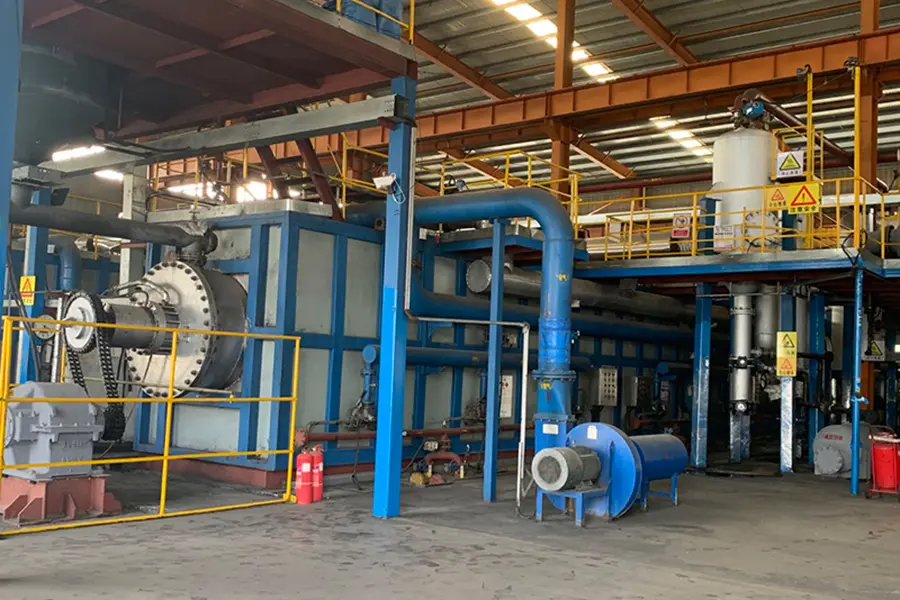
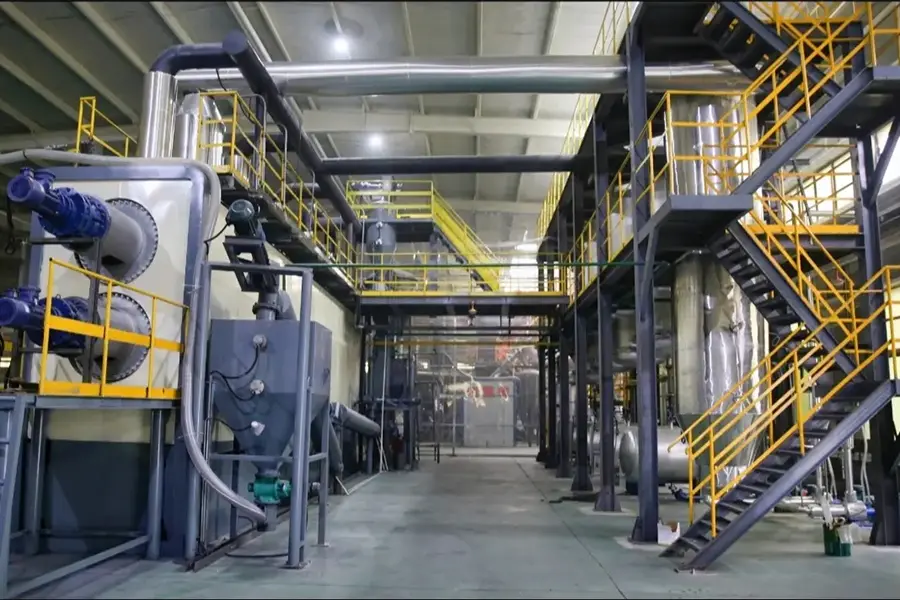
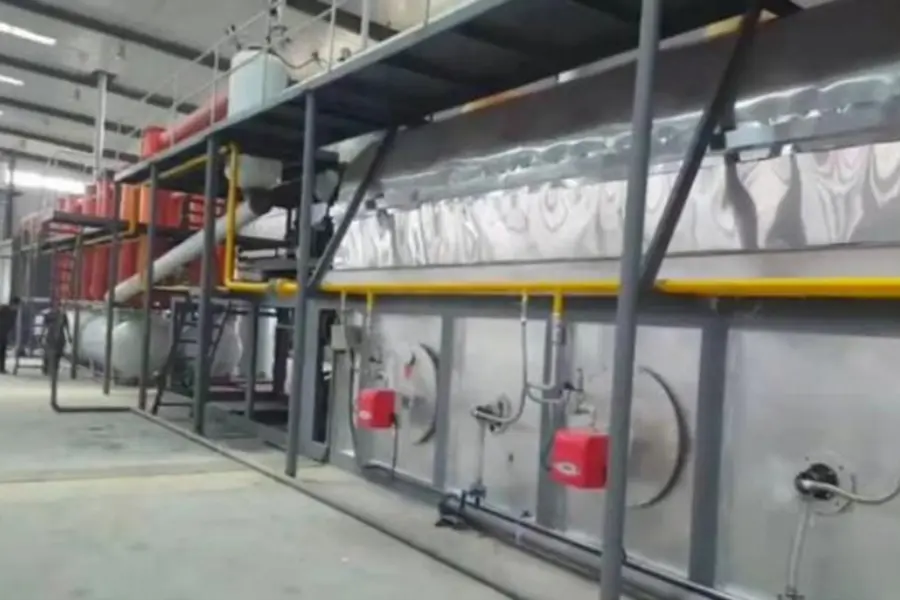
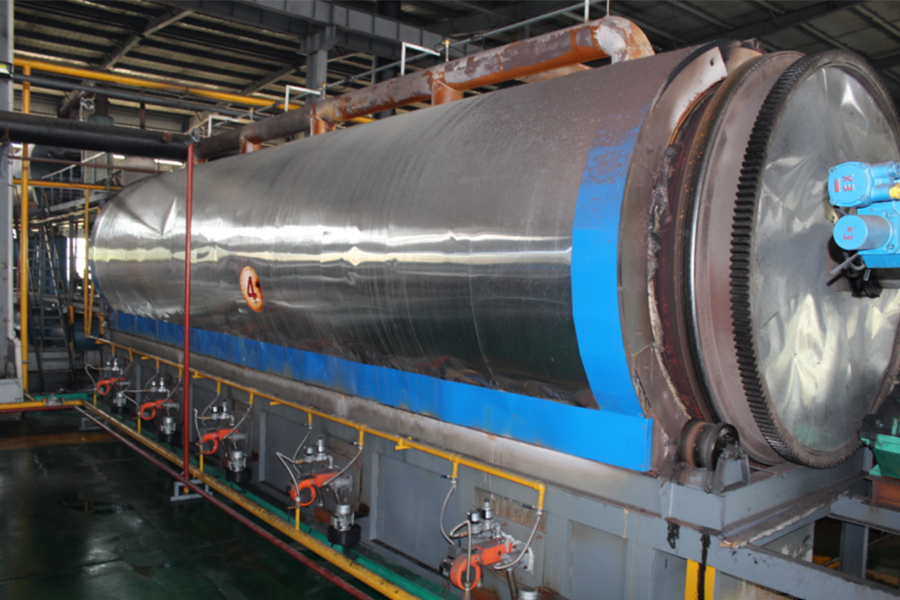
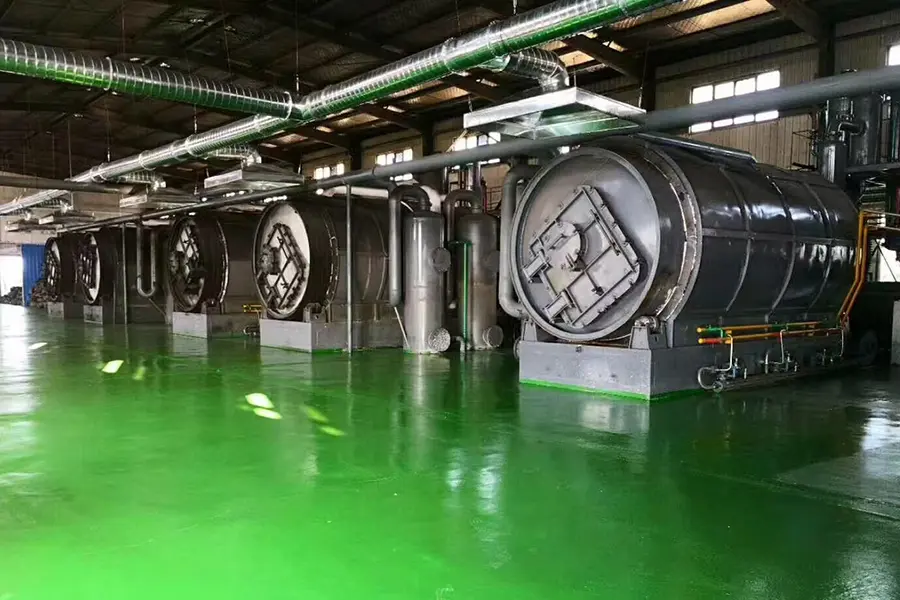
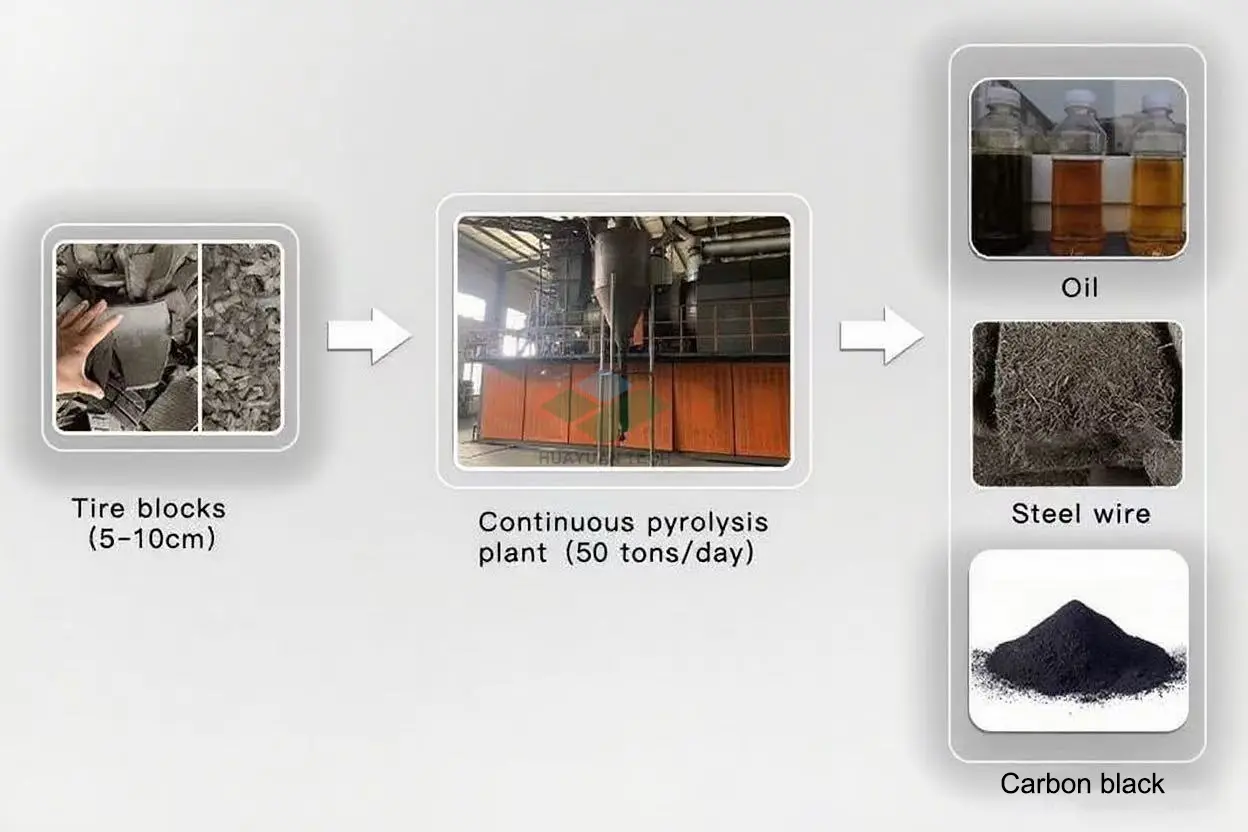
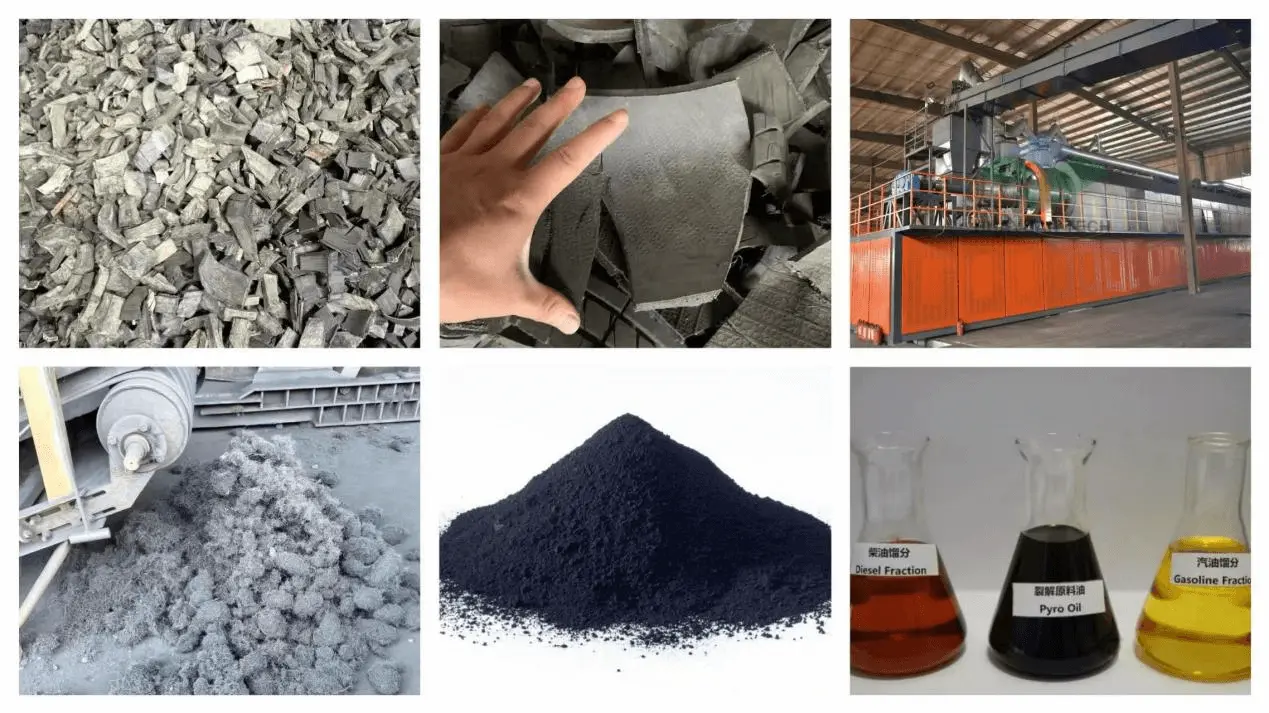
Continuous pyrolysis plant(5-10cm tire blocks as feedstock)
Video
Advantage
1. Unique rotary seal design, with a long maintenance free operating cycle.
2. Special process design ensures that the carbon powder after pyrolysis meets industry requirements.
3. An effective defocusing layout greatly extends the cleaning cycle of the equipment
4. An independent safety control system effectively detects gas leaks and system oxygen levels.
5. An efficient feed control system that prevents combustible gases from escaping while feeding
6. Adopt various forms of combination processes for different materials to better ensure safe and efficient production.
7. Achieve leak free sealing of rubber block feeding and solve the problem of sealing of mixed discharge of rubber powder and steel wire.
8. Realize constant temperature adjustable heating.
9. Achieved long-term effective operation of the sealing system.

Working principle
1. Pre processing steps:
The raw materials are shredded by a shredder and transformed into tire rubber blocks with a uniform size of 5-10cm, which are then transported to the feeding machine for preparation.
2. Pyrolysis process:
Press the start button to start the combustion engine and begin heating the pyrolysis kettle. After the pyrolysis kettle reaches the set temperature, the feeding machine starts to transport the raw materials into the pyrolysis chamber for pyrolysis. The feeding machine feeds according to the PLC indication variables to control the pressure and temperature inside the pyrolysis kettle. The normal operating temperature is between 400-420 degrees Celsius, and the normal pressure is 6-10Kp. The raw materials have their original solid state melted into liquid state by heating, and then decomposed into gas state and output from the outlet. The remaining impurities and ash are discharged from the tail slag extractor. The function of the pyrolysis kettle is to complete the phase transition process of the substance (solid liquid gas). The slag extractor is started to discharge the ash and impurities after pyrolysis, and the pyrolysis process is completed.
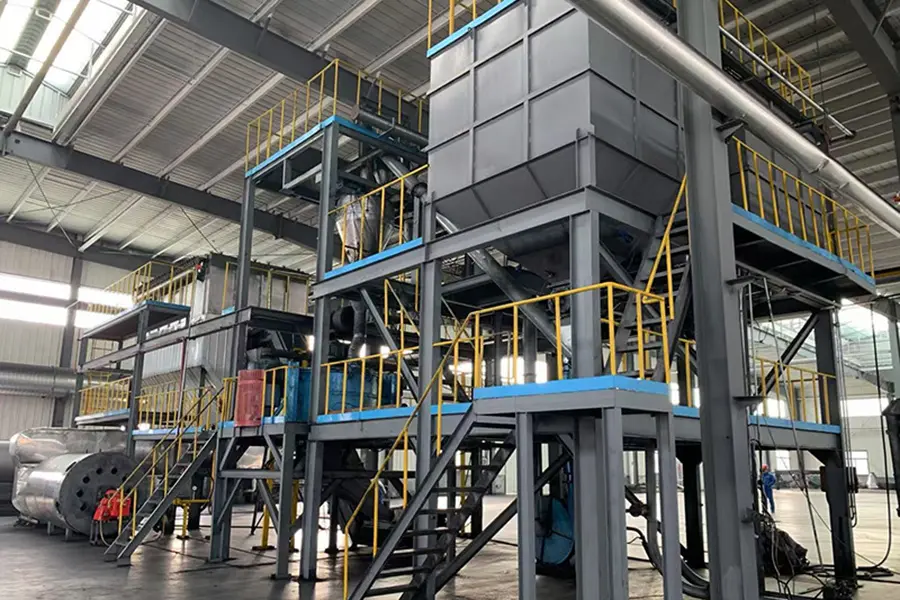
3. Thermal decomposition flue gas condensation purification:
After entering the condensation device, the high-temperature oil and gas are cooled by secondary water cooling to reduce the temperature to room temperature, transforming from a gaseous state to a liquid state. After condensation, it becomes a mixture of oil and gas, and after three-stage precipitation, impurities and ash are removed. The oil is separated into a storage tank through a three-stage separator, and the remaining combustible flue gas is purified by removing hydrogen chloride through a dechlorination and neutralization device.
4. Gas constant pressure storage:
The combustible gas is discharged into the gas storage tank for storage, undergoes precipitation and dehydration, and then undergoes three-stage precipitation before being transported to the constant pressure storage tank for storage and backup by a Roots blower.
5. Combustion heating:
When the pressure in the gas storage tank rises to 10KP, the main fuel valve closes, cutting off the external heat source supply. Start self circulating combustion, that is, burning the gas generated by oneself to heat oneself. The combustion chamber adopts a temperature gathering design, with a maximum working temperature of 1500 degrees, and the combustible gas is fully burned before meeting the emission standards.
6. Exhaust gas heat exchange:
The exhaust gas with a temperature of up to 380 degrees Celsius is cooled to 180 degrees Celsius through a heat exchanger before being discharged. The heat exchanged air is used for auxiliary combustion in the combustion engine, which plays a role in reducing emissions and saving energy.
7. Combustion exhaust gas treatment:
The exhaust gas is subjected to a first stage water bath dust removal to remove dust from the flue gas, followed by desulfurization and dust removal to remove sulfur elements from the flue gas, and then purified with fillers to remove odors
Post emission, emission standard GB/T32662-2016
Contact Us